As the proportion of distributed energy resources (DER) increases, and electrical vehicles are being deployed, the transmission and distribution electricity grids have to become smarter and more flexible, ensure reliability, and improve efficiency. Also, there is an opportunity for loads and generators to offer novel services to support the grid or local interests.
Therefore, a Smart Energy system is required to reach these targets, including not only a smart grid but also taking the opportunity for loads and generators to offer novel services supporting the system. Based on a convergence of energy grids and telecommunication networks, enabling a real-time monitoring and control of the energy system, the main system objectives include balancing production and consumption, maximizing DER integration (local or global), reducing energy bills, identifying and fixing grid issues and anticipating grid maintenance needs.
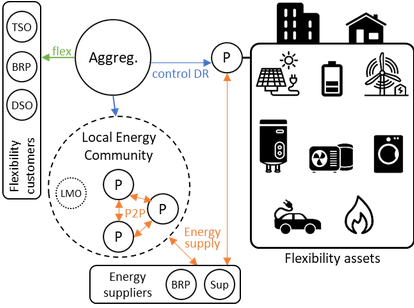
Fig. x ~ Future smart energy system, leveraging flexibility
Based on its strong knowledge of smart metering and e-mobility, Trialog is working on smart energy systems since 2012 via several research and innovation projects but also industrial projects around grid observability, advanced grid control, flexibilities, local energy communities, energy storage, energy management, vehicle-to-grid, smart home, smart building, … and associated horizontal technologies such as semantic interoperability, internet of things, data spaces, digital twin, …
Trialog also supports the ecosystem by contributing to EU initiatives such as BRIDGE and ETIP SNET and international standardization committees.
Trialog’s main added value focuses on architecture, design, validation and deployment phases, offering tools and support on system architecture and modeling (incl. SGAM), smart grid standards, cyber-security, interoperability and system validation.
Reference documents:
The table below lists important references for the smart energy domain. The documents to which we have contributed are marked with an asterisk.
| Titre du doc | Organisation | Lien | Auteur |
|---|---|---|---|
| European (energy) data exchange reference architecture 3.0 | BRIDGE | Link | * |
| Reference Framework | BRIDGE | Link | * |
| ETIP SNET, R&I implementation plan 2022-2025 | ETIP SNET | Link | |
| Data Spaces for Energy, Home and Mobility | OPEN-DEI | Link | * |
| Design principles for Data Spaces | IDSA | Link | * |
| Interoperability Framework in Energy Data Spaces | IDSA | Link | * |
| Common European Energy Data Space | EnTEC | Link | |
| Code of Conduct on energy management related interoperability of Energy Smart Appliances | JRC | Link | |
| Implementing Regulation on interoperability requirements and non-discriminatory and transparent procedures for access to metering and consumption data | SGTF | Link |
| Titre du papier | Journal/Conf | Lien |
|---|---|---|
| Towards an interoperability roadmap for the energy transition | e & i Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik (July 2023) | Link |
| How to ensure interoperability in demand response systems: the examples of the European projects H2020 GIFT and MAESHA | 27th International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2023) | Link |
| EV-based flexibility for grid operators | 11th Symposium Communications for Energy Systems (ComForEn 2021) | Link |
| SAREF-Compliant Knowledge Discovery for Semantic Energy and Grid Interoperability | 2021 IEEE 7th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT) | Link |
| Fostering the relation and the connectivity between smart homes and grids – InterConnect project | CIRED 2020 Berlin Workshop | Link |
| Identification of common services in European Flexibility Demonstrators for Laboratory-based Interoperability Validation | 2019 8th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA) | Link |
| SGAM-Based Comparative Study of Interoperability Challenges in European Flexibility Demonstrators: Methodology And Results | 2018 IEEE 16th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN) | Link |